Indexes are called keys in MySQL. They are data structures that storage engines use to find rows quickly, leading to a better performance for your queries.
They are very important for higher performance when your data is quite large. Indexes are often misunderstood. So, poor indexing can cause lots of performance problems. Indexes can improve performance by many orders of magnitude.
Let us look at some of the cases where indexes can be helpful.
- Indexes help to find rows matching a WHERE clause,
- Eliminate rows by opting for the MOST selective index,
- Retrieving rows from other tables while joining multiple tables,
- Finding MIN or MAX values from table columns,
- Sorting or grouping tables.
- A covering index is very helpful to reduce an I/O bottleneck.
Well, this is a list of a few of the things where indexes are very effective to improved performance. Let's understand most of this with the help of demonstrations next.
Let's start.
Here we are in the MySQL Workbench and in this very first example, we will understand the basics of indexes.
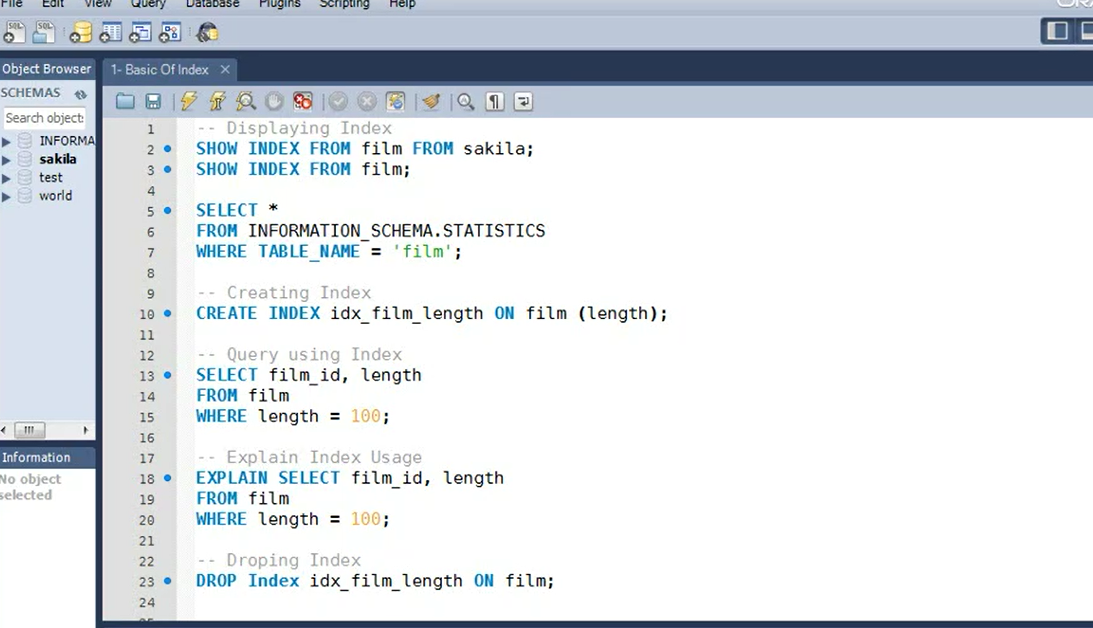
If you want to know if any table has an index or not, you can use the command
SHOW INDEX.
For example, if you want to see all the indexes of film table from sakila database, you can run this SHOW INDEX command.
SHOW INDEX FROM film FROM sakila.
First FROM film indicates the name of the table, and the second FROM film indicates the name of the database.
You can select the statement and click on Execute.
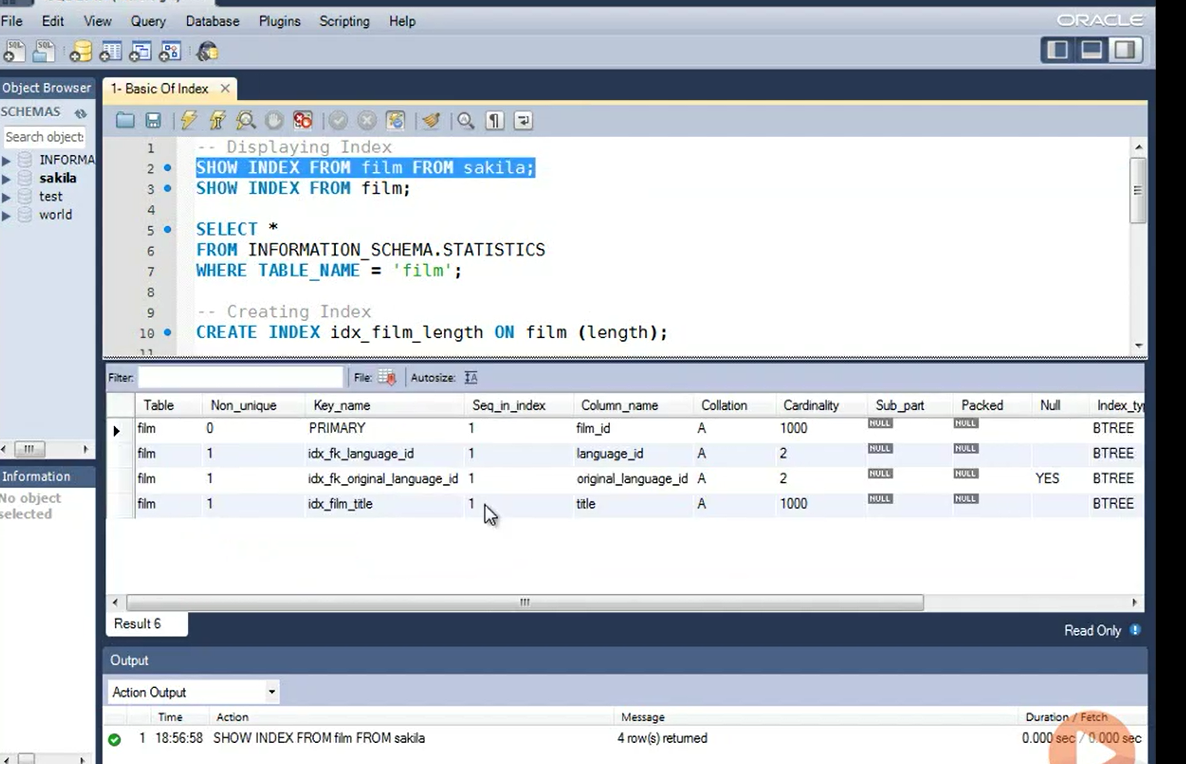
In the result output, there are four rows.
The first row is for PRIMARY key and the rest of the three rows are for non-PRIMARY keys.
The first column indicates the name of the table, which is Film over here.
The Column_name on which PRIMARY key is created is film_id.
Cardinality of that is 1000. That means there are a 1000 different values in this column.
When we scroll further, we can see a column called Index_type.
On the table film of sakila database, all the indexes are of type BTREE. In simpler words, film table has four indexes.
First, on film_id, second on language_id, third on original_ language_id, and fourth on title.
If the context of your query is sakila database already, you can just write SHOW INDEX FROM film to list all the indexes on this table as well.
Here is one more method how you can list all the indexes on the table film.
We'll be retrieving data from INFORMATION_SCHEMA. STATISTICS table.
INFORMATION_SCHEMA is the information database, the place that stores information about all the other databases that the MySQL server maintains.
Inside INFORMATION_SCHEMA, there are several read-only tables.
They are actually views, not base tables, so there are no files associated with them and you cannot set any events or triggers on them.
We can read the contents of INFORMATION_SCHEMA table, but cannot perform INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE operations over it.
INFORMATION_SCHEMA.
STATISTICS table provides us information about table indexes.
Let's select this entire statement and click on Execute.
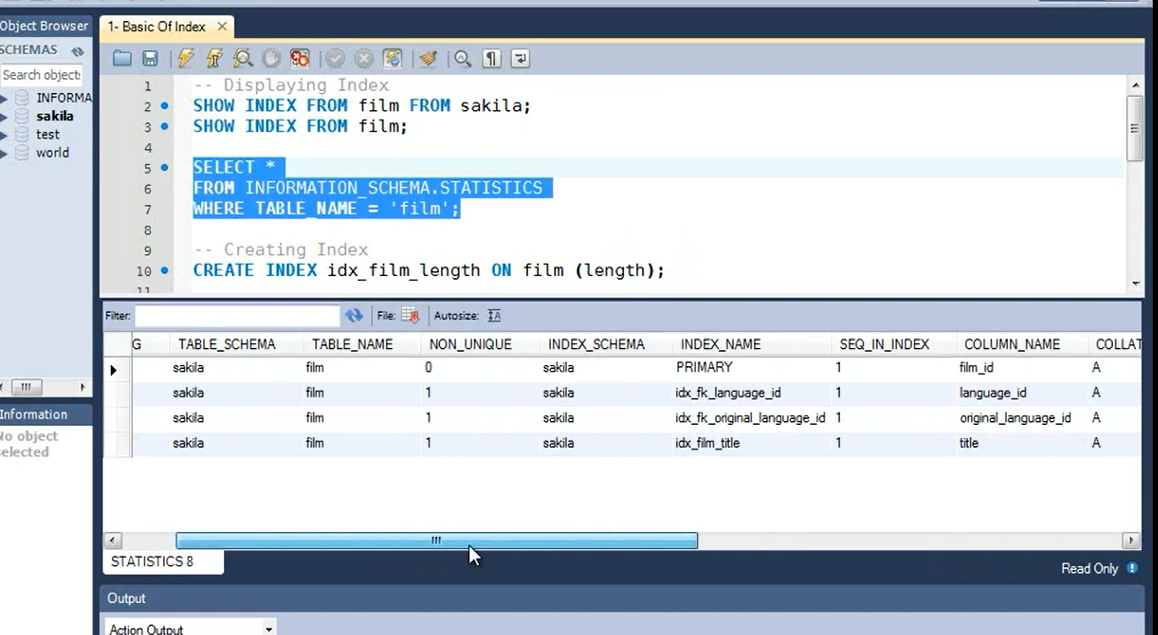
Well, on a quick look, we can see that the result is very similar to what we have seen earlier. However, the column placements are a little different than earlier results.
Here is TABLE_SCHEMA, which is sakila, TABLE_NAME is film, and here is NON_UNIQUE column. The name of the index is listed in this column and columns which are used in indexes are listed over here.
CARDINALITY is also listed in this column.
On further scrolling right, we can also see type of index. Personally, I have no preference.
Both of them always retrieve accurate information. Use the one which you find easy to remember.